'
Leonardo da Vinci

- Leonardo da Vinci was born on April 15, 1452, in the small town of Vinci, Italy.
- He was an illegitimate child, born to a wealthy notary named Piero Fruosino di Antonio da Vinci and a peasant woman named Caterina.
- Leonardo was left-handed and often wrote in mirror script, which was difficult to read.
- He conducted dissections of around 30 human corpses to study anatomy, making groundbreaking discoveries.
- Leonardo was a vegetarian and believed in the ethical treatment of animals
'
Business Ventures
- Leonardo da Vinci's Business Ventures ranged from painting and sculpting to designing weapons and engineering projects.
- He had a successful career as an artist, working for powerful patrons like the Medici family and the Duke of Milan.
- da Vinci also worked as a military engineer, designing fortifications and weapons for his patrons.
- He had a keen interest in inventions, designing concepts for machines like a flying machine, a diving suit, and a mechanical lion.
- Leonardo da Vinci's artistic and engineering talents made him a versatile and successful entrepreneur during his time.
'
Endorsements
- Da Vinci was involved in numerous engineering and scientific projects, providing designs and consulting services to wealthy patrons, effectively acting as a business consultant.
- He designed and built various machines for the Sforza family of Milan, including war machines, hydraulic devices, and automated spectacles.
- He received payments for his inventions and designs, creating a revenue stream.
- His engineering designs were frequently endorsed by Duke Ludovico Sforza of Milan, who recognized their strategic value.
- He created designs for a new type of crossbow, receiving commissions based on its potential military applications.
- Da Vinci's designs for canal systems and water management were sought after for improving agricultural productivity, representing endorsements of his technical expertise.
- He collaborated with architects on building projects, offering his design expertise and securing contracts.
'
Support from Wealthy Patrons
- Leonardo da Vinci was able to pursue his artistic endeavors with the support of wealthy patrons such as the Medici family in Florence.
- These patrons provided Leonardo with financial backing, materials, and opportunities to create some of his most famous works, such as the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper.
- Support from wealthy patrons was crucial for many artists during the Renaissance period, as it allowed them to focus on their craft without having to worry about financial concerns.
- Through his relationships with wealthy patrons, Leonardo was able to gain recognition and fame as an artist, earning him a reputation as one of the greatest minds of his time.
'
Investments
- Da Vinci invested heavily in the silver mines of Milan, a venture that proved largely unsuccessful.
- He invested in the production of salt, seeking to capitalize on the growing demand for the commodity.
- He made significant investments in the glass industry, including the production of colored glass.
- Da Vinci invested in a silk manufacturing venture, attempting to establish a textile industry in Milan.
- He had an interest in the production of mirrors, a rapidly growing market at the time.
- Da Vinci invested in various artistic and mechanical inventions, often seeking funding for his projects.
'
Funding for Art and Science Projects
- Leonardo da Vinci was a famous Italian artist, scientist, and inventor during the Renaissance period.
- He is known for iconic works of art such as the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper.
- Da Vinci was also a pioneer in the fields of anatomy, engineering, and astronomy.
- His interdisciplinary approach to art and science continues to inspire creativity and innovation today.
- Da Vinci's business ventures and investments often supported his ambitious art and science projects.
- His diverse interests and accomplishments have left a lasting legacy in the worlds of art, science, and technology.
'
Production Companies
- Signa Da Vinci: Da Vinci established a production company, Signa Da Vinci, in Florence in 1504.
- The company primarily focused on the production of pigments, varnishes, and paints.
- It also produced various art materials, including drawing tools and paper.
- Signa Da Vinci supplied materials to artists throughout Italy, including Michelangelo and Raphael.
- The company operated until da Vinci's death in 1519.
'
Career

- Leonardo da Vinci was a painter, sculptor, architect, writer, anatomist, geologist, astronomer, botanist, inventor, engineer, and scientist, epitomizing the Renaissance man.
- He created some of the most famous artworks in history, including the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper.
- Leonardo worked for powerful patrons, including Ludovico Sforza, the Duke of Milan, and King Francis I of France.
- He made significant contributions to anatomy through his detailed sketches and dissections, which were revolutionary for their time.
- Leonardo's notebooks contain numerous inventions and ideas, many of which were ahead of his time, such as designs for flying machines and military equipment. more...
'
Art
- Da Vinci began his artistic career as an apprentice to Andrea del Verrocchio in Florence.
- He produced a vast number of paintings, drawings, and sketches throughout his career.
- Notable paintings include the *Mona Lisa*, *The Last Supper*, and *Virgin of the Rocks*.
- He employed techniques like sfumato and chiaroscuro to create realistic and atmospheric effects in his paintings.
- His art demonstrated innovative perspectives and anatomical accuracy, influencing future generations of artists.
'
Paintings
- Leonardo da Vinci is considered one of the greatest painters of all time.
- He is known for iconic paintings such as the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper.
- Leonardo da Vinci's painting technique involved meticulous attention to detail and realistic portrayal of subjects.
- His paintings are highly sought after and valued, with some selling for millions of dollars.
- Leonardo da Vinci's works have influenced countless artists and continue to be studied and admired centuries after his death.
'
Adoration of the Magi

- Leonardo da Vinci painted the "Adoration of the Magi" between 1481 and 1482, during his early career in Florence, Italy.
- The painting features the traditional biblical scene of the Magi or Wise Men bringing gifts to the infant Jesus.
- Leonardo's "Adoration of the Magi" is considered unfinished, as he left the work to focus on other projects and never completed it.
- The painting showcases Leonardo's innovative use of perspective and composition, with rich details and symbolic elements throughout the scene.
- "Adoration of the Magi" is now housed in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence, where it is revered as an important piece in the history of art.
'
Annunciation
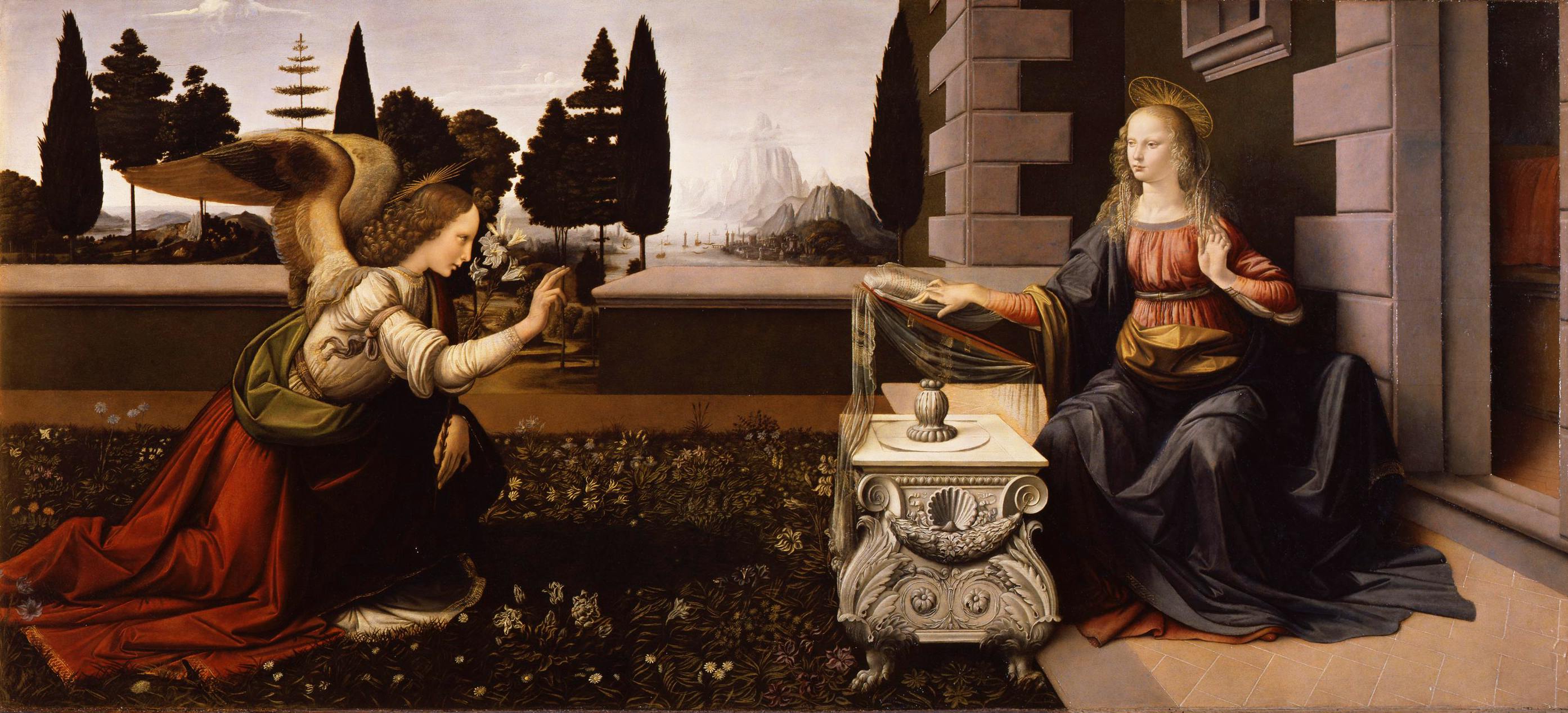

- The Annunciation is a religious event in Christian tradition that commemorates the visit of the archangel Gabriel to the Virgin Mary to inform her that she would conceive and give birth to Jesus, the Son of God.
- Leonardo da Vinci's painting titled "The Annunciation" is one of his most famous works and is housed in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence, Italy.
- The painting features exquisite details and symbolism, such as the lilies symbolizing Mary's purity and the book representing her acceptance of the news brought by the angel.
- Leonardo da Vinci's mastery of light and shadow is evident in "The Annunciation," with the use of chiaroscuro creating a sense of depth and realism in the painting.
'
Benois Madonna

- The Benois Madonna is a painting by the Italian Renaissance artist Leonardo da Vinci.
- It is believed to have been painted between 1478 and 1480.
- The painting is also known as Madonna and Child with Flowers.
- It is currently housed in the State Hermitage Museum in St. Petersburg, Russia.
- The Benois Madonna is considered to be one of Leonardo da Vinci's early works.
'
Ginevra de' Benci

Below are some interesting facts about the painting "Ginevra de' Benci" by Leonardo da Vinci:
- Ginevra de' Benci is considered one of Leonardo da Vinci's earlier works and is believed to have been painted when he was still in his twenties.
- The painting is a portrait of a young Florentine woman named Ginevra de' Benci, who was a member of a prominent family.
- Leonardo da Vinci's technique in this painting is characterized by his precise attention to detail and subtle use of light and shadow.
- The portrait is unique in that it shows Ginevra in a three-quarter view, a departure from the traditional profile portraits of the time.
- The intricate landscape background in the painting is thought to be symbolic and meaningful, possibly representing Ginevra's virtues or qualities.
'
La Belle Ferronnière

- La Belle Ferronnière is a portrait of a woman believed to be a mistress of Leonardo da Vinci, painted in the early 16th century.
- The painting is also known as Portrait of an Unknown Woman and is currently housed in the Louvre Museum in Paris.
- It is considered one of Leonardo da Vinci's most famous works and showcases his mastery of portraiture and attention to detail.
- The identity of the woman in the painting is still debated among art historians, adding to the mystery and allure of the artwork.
- La Belle Ferronnière is renowned for its captivating gaze and enigmatic smile, reminiscent of da Vinci's most famous painting, the Mona Lisa.
'
La Scapigliata

- La Scapigliata is an unfinished painting by Leonardo da Vinci, believed to have been painted in the early 1500s.
- The painting's name, "La Scapigliata," means "The Lady with Disheveled Hair" in Italian.
- It is currently housed in the National Museum of Parma, Italy.
- The artwork is highly regarded for its innovative composition and depiction of a female figure with flowing hair.
- Leonardo da Vinci's exceptional attention to detail and mastery of light and shadow can be seen in this painting.
'
Lady with an Ermine

- Lady with an Ermine is a portrait painting by Leonardo da Vinci.
- It is believed to have been painted around 1489–1490.
- The painting depicts Cecilia Gallerani, a young woman from the Milanese court.
- It is renowned for its innovative composition and the detailed rendering of the ermine.
- Lady with an Ermine is housed at the Czartoryski Museum in Kraków, Poland.
'
Mona Lisa

- Leonardo da Vinci started painting the Mona Lisa in 1503 and worked on it for several years, making numerous adjustments.
- The painting is believed to be a portrait of Lisa Gherardini, the wife of a wealthy Florentine merchant.
- Leonardo never delivered the painting to the Giocondo family; he kept it with him until his death.
- The Mona Lisa was stolen from the Louvre in 1911 and recovered two years later, which significantly boosted its fame.
- Despite its immense cultural impact, the Mona Lisa is relatively small, measuring just 30 inches by 21 inches. more...
'
Portrait of a Musician
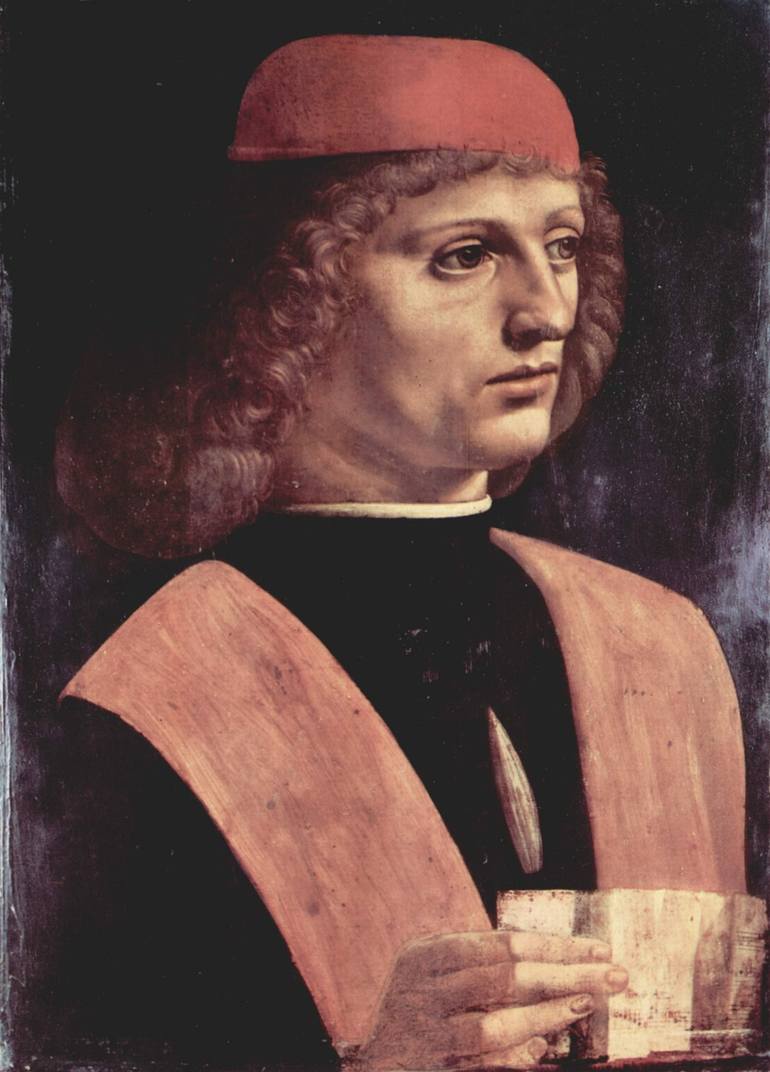

- The Portrait of a Musician is a famous artwork created by the renowned Italian artist Leonardo da Vinci.
- It is believed to have been painted around 1485 and is currently housed in the Pinacoteca Ambrosiana in Milan, Italy.
- The painting depicts a young musician holding a lira da braccio, which was a popular musical instrument during the Renaissance period.
- Leonardo da Vinci was known for his attention to detail and mastery of shading and perspective, which is evident in this portrait.
- The Portrait of a Musician is considered a prime example of da Vinci's ability to capture emotion and expression in his subjects.
'
Portrait of Isabella d'Este

Portrait of Isabella d'Este
- The Portrait of Isabella d'Este is a famous painting by Renaissance artist Leonardo da Vinci.
- Isabella d'Este was a prominent noblewoman, known for her intelligence, political acumen, and patronage of the arts.
- The painting is believed to have been created around 1499-1500, during Leonardo's time in Milan.
- Isabella d'Este was the Marchioness of Mantua and a key figure in the Italian Renaissance cultural scene.
- Leonardo's portrait of Isabella d'Este is known for its detailed depiction of the sitter's features and elegant pose.
'
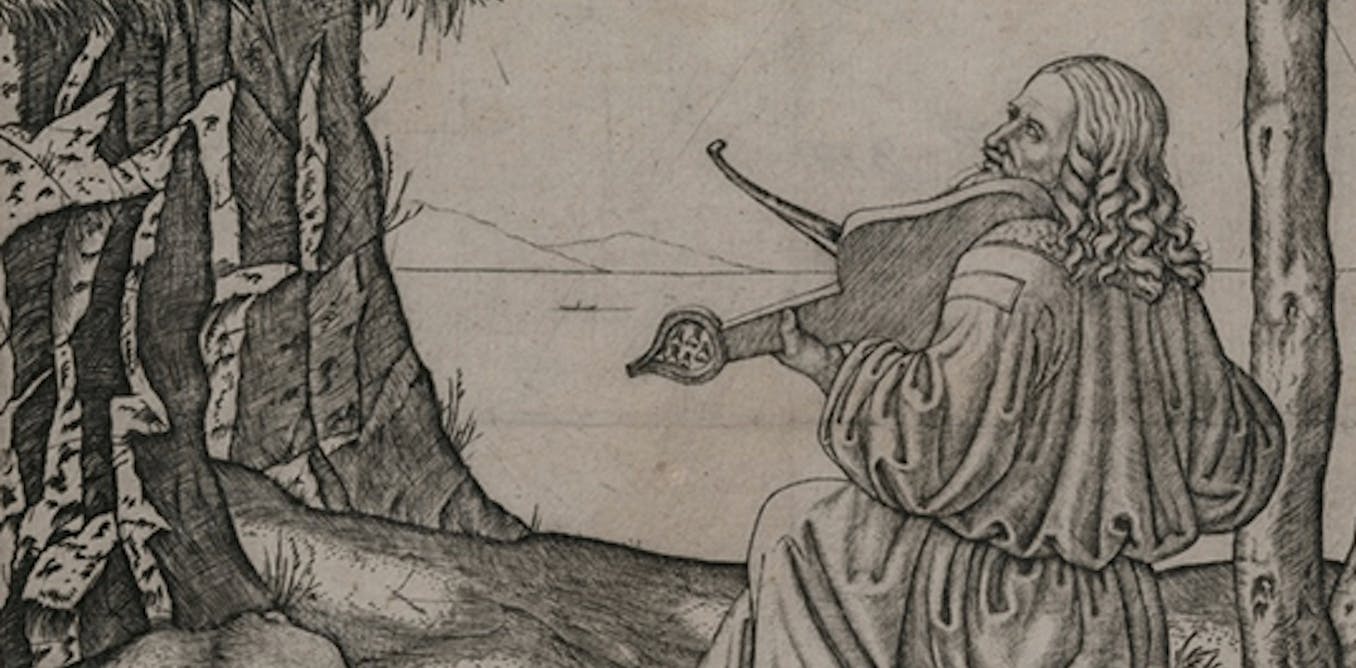
Saint Jerome in the Wilderness

- Saint Jerome in the Wilderness is a painting by Italian artist Leonardo da Vinci.
- It is believed to have been created around 1480.
- The painting depicts Saint Jerome, a Christian scholar and translator, in the wilderness.
- Saint Jerome is shown in meditation, symbolizing his ascetic life and dedication to study and prayer.
- The background of the painting includes a vast landscape with a lion as a companion to Saint Jerome.
'
Saint John the Baptist

- Saint John the Baptist is a key figure in Christianity, known for baptizing Jesus in the Jordan River.
- Leonardo da Vinci's painting of Saint John the Baptist depicts him as youthful, with long wavy hair and a staff.
- There is a sense of mystery and enigma in Leonardo's portrayal of Saint John the Baptist, typical of his work.
- The painting is housed in the Louvre Museum in Paris and is considered one of Leonardo's most famous works.
'
Salvator Mundi

- Leonardo da Vinci was a painter, sculptor, architect, scientist, inventor, and more.
- His career spanned several decades, primarily in Florence and Milan.
- Da Vinci's artistic style was characterized by sfumato, chiaroscuro, and anatomical accuracy.
- He famously worked on the *Mona Lisa*, *The Last Supper*, and *Salvator Mundi*.
- The *Salvator Mundi* is a painting of Jesus Christ holding a globe in his hands.
- It was painted by Leonardo da Vinci between 1499 and 1515.
- The painting is believed to be one of the last works da Vinci completed.
- It was sold at Christie’s in 2017 for $450.3 million, making it the most expensive artwork ever sold.
'
The Adoration of the Magi

- Leonardo da Vinci's painting "The Adoration of the Magi" is believed to have been started around 1481 when he was in his late 20s and remained unfinished at the time of his death.
- The painting depicts the scene of the Adoration of the Magi, where the three wise men are presenting gifts to the infant Jesus.
- Leonardo's depiction of the Virgin Mary in the painting is thought to be a portrait of his own mother, Caterina.
- "The Adoration of the Magi" showcases Leonardo's use of perspective and intricate details, reflecting his mastery of the Renaissance art style.
- The painting showcases Leonardo's fascination with the human form and his ability to capture emotions and expressions in his subjects.
'
The Baptism of Christ

Here are some interesting facts about Leonardo da Vinci's painting "The Baptism of Christ":
- The Baptism of Christ was painted by Leonardo da Vinci and his mentor Andrea del Verrocchio around the year 1475-1478.
- This painting is considered one of Leonardo's early works and showcases his talent as a young artist.
- It is believed that Leonardo painted the angel on the left side of the painting, while Verrocchio painted the figure of Jesus in the center.
- The painting depicts the biblical scene of the baptism of Jesus by John the Baptist in the River Jordan.
- Leonardo's use of light and shadow in this painting is considered innovative for the time and demonstrates his skill in creating depth and realism.
'
The Last Supper
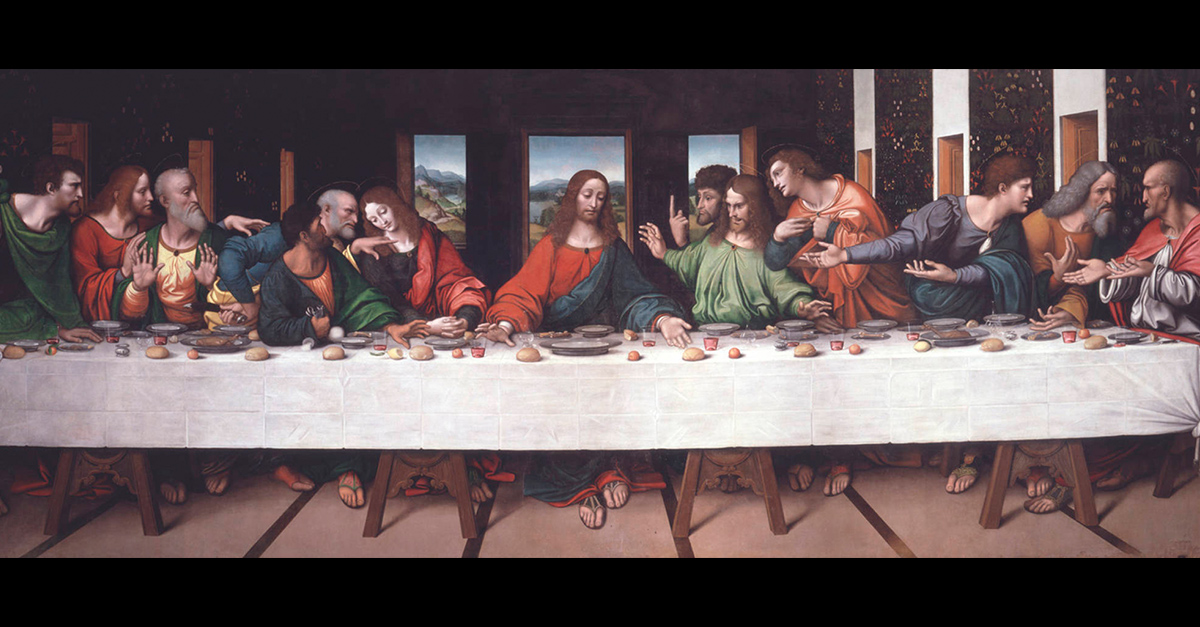

- Leonardo da Vinci completed "The Last Supper" between 1495 and 1498.
- The painting depicts the last meal Jesus shared with his apostles before his crucifixion.
- "The Last Supper" is located in the Convent of Santa Maria delle Grazie in Milan, Italy.
- It is considered one of the greatest masterpieces of Italian Renaissance art.
- The size of the painting is approximately 15 ft × 29 ft.
'
The Virgin and Child with Saint Anne

- Leonardo da Vinci's painting "The Virgin and Child with Saint Anne" is also known as "Madonna and Child with Saint Anne".
- The painting depicts the Virgin Mary, the Christ Child, and Mary's mother Saint Anne.
- It is believed to have been painted between 1503 and 1519 during Leonardo's time in Florence and France.
- The painting is considered a masterpiece of Renaissance art, showcasing Leonardo's skill in composition and storytelling.
- "The Virgin and Child with Saint Anne" is housed in the Louvre Museum in Paris, France.
'
The Vitruvian Man

Here are some interesting facts about The Vitruvian Man:
- Leonardo da Vinci created The Vitruvian Man as a study on the proportions of the human body, based on the writings of the Roman architect Vitruvius.
- The drawing is also known as "The Proportions of Man" and is considered one of da Vinci's most iconic works.
- The Vitruvian Man depicts a male figure in two superimposed positions with his arms and legs outstretched within a circle and square, demonstrating geometric and proportionate relationships.
- It is a symbol of the concept of the "perfect" or "ideal" human body and its relationship to the universe.
- The Vitruvian Man is housed in the Gallerie dell'Accademia in Venice, Italy, and is considered a cultural and scientific masterpiece.
'
Virgin of the Rocks
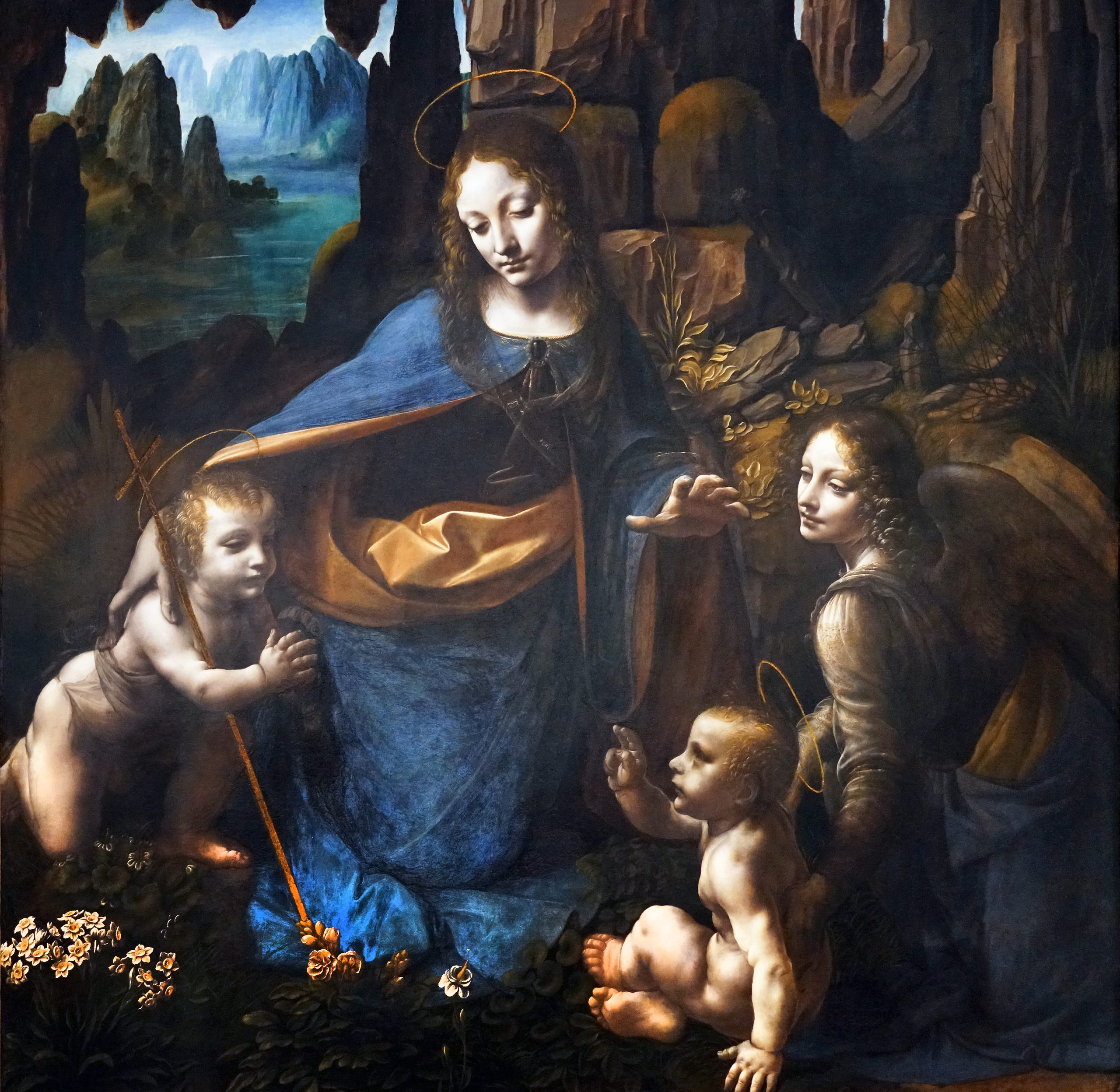

- The Virgin of the Rocks is a famous painting by Leonardo da Vinci, created between 1483 and 1486.
- There are two versions of the painting, with one housed in the Louvre, Paris, and the other in the National Gallery, London.
- The painting depicts the Madonna, the Christ Child, the infant John the Baptist, and an angel in a rocky setting.
- Leonardo da Vinci employed his innovative technique of sfumato to create a sense of depth and atmosphere in the painting.
- The mysterious and enigmatic composition of the painting has sparked numerous interpretations and debates among art historians.
'
Engineering
- Da Vinci designed numerous inventions, many of which were centuries ahead of their time.
- He conceived of designs for flying machines, including ornithopters and rudimentary helicopters.
- He developed plans for tanks, armored vehicles, and other military technologies.
- His studies of fluid dynamics led to designs for canals, irrigation systems, and water pumps.
- He designed machines for mining, such as a steam-powered excavation device.
- He created a design for a diving suit, incorporating elements of pressure equalization.
- Da Vinci explored concepts of gear trains and mechanical automation in his designs.
- He investigated the principles of leverage and mechanical advantage.
- His work on the Sforzando canal in Milan exemplifies his engineering skills.
- He produced detailed sketches and models to visualize his inventions.
'
Inventions
- Leonardo da Vinci was credited with inventing the concept of the helicopter, over 400 years before it became a reality.
- He designed a robotic knight for pageants, which could sit, stand, and move its head.
- Da Vinci created plans for a machine that could be considered an early version of a tank, with a platform for cannons and other weapons.
- One of his most famous inventions is the parachute, which he designed as a means of escaping from a burning building.
- Leonardo da Vinci also developed a mechanical lion that could walk and move its head, created for a royal celebration in France.
'
Armored Vehicle

- Leonardo da Vinci conceived of a design for an armored vehicle, often referred to as a "carro armato" (armored chariot).
- The design, documented in his notebooks, envisioned a heavily armored vehicle with rotating wheels for maneuverability.
- It featured a central compartment protected by iron plates, likely for the commander.
- The vehicle’s rotating wheels were intended to allow it to turn in place, a revolutionary concept for the time.
- There is no evidence that da Vinci ever built a working prototype of this armored vehicle. It remained a theoretical design in his notebooks.
- The design incorporated a crew of several men, and included features like a defensive covering for the crew.
- Da Vinci's design was significantly ahead of its time, anticipating many features later found in modern armored vehicles.
'
Flying Machine

- Leonardo da Vinci conceptualized the Flying Machine as a mechanical device designed to fly and imitate the flight of birds.
- His Flying Machine design included a wingspan of over 33 feet and was based on the anatomy of a bat.
- Leonardo's Flying Machine design featured a pilot lying prone on a board and using hand-cranked wings to generate lift and propulsion.
- While Leonardo's Flying Machine was never built or tested during his lifetime, modern replicas have successfully demonstrated its potential for flight.
'
Parachute

- Leonardo da Vinci is credited with designing one of the earliest known parachute designs in the late 15th century.
- His parachute design, sketched in 1485, utilized a conical-shaped fabric canopy supported by a central rope.
- The design featured a rudimentary harness system to attach the device to the user.
- Da Vinci's parachute was intended for use in descending from tall structures, though its practical application was limited by the materials and construction techniques of the time.
- While the exact construction details are debated, the sketch clearly illustrates a device designed to slow a person's descent.
'
Scuba Gear
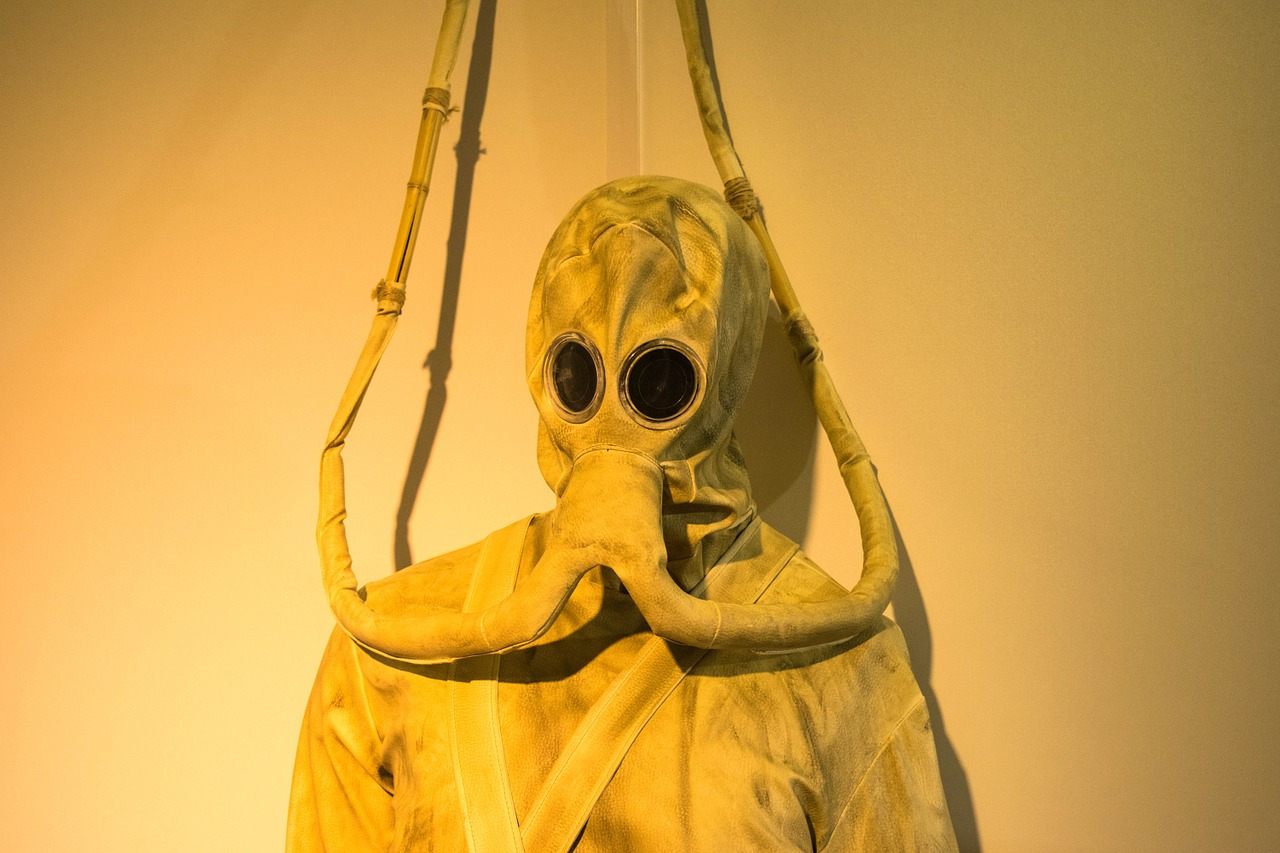

- Around 1472-1475, Leonardo da Vinci began designing what is considered the earliest conceptual design of scuba gear.
- His design incorporated a leather diving suit with a helmet, utilizing a system of air pumps and valves to maintain underwater pressure.
- The design included a bellows-like device for supplying air, a method for controlling air pressure, and a rudimentary valve system.
- While the technology of the time wasn't capable of creating a fully functional system, da Vinci's sketches demonstrate an understanding of the principles required for compressed air diving.
- The sketches indicate a complex system to prevent the leather suit from collapsing under water pressure.
- The design showcases his meticulous attention to detail and his forward-thinking approach to engineering challenges.
'
Science
- Da Vinci conducted extensive anatomical studies, including dissections of human corpses, to understand human musculature and skeletal structure.
- He meticulously documented his observations in detailed drawings and notes, pioneering anatomical illustration.
- He investigated fluid dynamics, studying the flow of water and air, leading to early observations of aerodynamics.
- Da Vinci designed and built various mechanical devices, showcasing an understanding of levers, gears, and pulleys.
- He studied optics, experimenting with light and shadow to achieve realistic effects in his paintings.
- He studied botany, meticulously documenting the structure and growth of plants.
- He investigated geology, analyzing rock formations and seeking to understand the Earth’s structure.
- Da Vinci explored the principles of perspective in art and engineering.
- He investigated the properties of metals and alloys.
- He conducted experiments on the strength of materials.
'
Anatomy
- Anatomy is the branch of science that deals with the structure of living beings.
- Leonardo da Vinci was a renowned Renaissance artist and scientist who made significant contributions to the field of anatomy.
- Leonardo da Vinci conducted dissections on human cadavers to study the intricate details of the human body.
- His anatomical drawings were highly detailed and provided valuable insights into the human anatomy.
- Leonardo da Vinci's studies in anatomy helped pave the way for advancements in medical science.
'
Anatomical Sketches

- Leonardo da Vinci was a renowned artist, scientist, and inventor of the Renaissance period.
- His anatomical sketches are highly detailed and accurate, showcasing his curiosity and dedication to understanding the human body.
- Leonardo da Vinci believed that studying anatomy was crucial for his art, as it helped him accurately portray the human form.
- His anatomical drawings were often ahead of his time and contributed greatly to the field of medical science.
- Leonardo da Vinci's sketches of the human body have been studied and admired by artists and scientists for centuries.
'
Human Body Dissections

- Leonardo da Vinci was a prolific and exceptionally talented Italian polymath of the High Renaissance.
- His career spanned painting, sculpture, architecture, geology, anatomy, invention, and writing.
- Da Vinci's scientific pursuits often stemmed from a desire to understand the natural world and apply that knowledge to his art and inventions.
- He meticulously studied human anatomy, believing a deep understanding of the body was crucial for realistic representation in his paintings.
- Da Vinci conducted numerous human body dissections, a highly controversial and often illegal activity at the time.
- He documented his findings from dissections in detailed anatomical drawings, significantly advancing the understanding of human musculature, bone structure, and internal organs.
- His dissections included those performed on cadavers procured through various channels, often involving deception or the use of bodies of those who had died in prison or from disease.
- He identified and accurately depicted the nervous system, circulatory system, and skeletal structures within the human body.
- His anatomical studies challenged prevailing Galenic theories about the human body.
- Da Vinci's drawings include extremely detailed representations of the skull, heart, brain, muscles, and nerves.
'
Botany

- Da Vinci meticulously studied plant anatomy, often dissecting flowers and plants.
- He created incredibly detailed drawings of plant structures, including roots, stems, leaves, and blossoms.
- His botanical drawings demonstrated a remarkable understanding of vascular systems and the arrangement of cells within plants.
- He documented the growth cycles of plants, including seed germination and the progression of leaf development.
- Da Vinci's observations of plant movement, particularly the response of flowers to sunlight (nastic movement), were pioneering.
- He explored the relationship between light and photosynthesis, though he didn't fully understand the process.
- His studies of plant reproduction, including pollination and seed dispersal, were among the earliest documented.
- He examined the structural adaptations of plants for survival, like the defense mechanisms of thorny plants.
'
Hydraulics

- Leonardo da Vinci designed and studied complex water systems, including canals, locks, and fountains.
- He investigated the principles of fluid dynamics, particularly buoyancy and pressure.
- Da Vinci's sketches reveal an understanding of Archimedes' principle, though not explicitly articulated.
- He devised a water-powered device resembling a primitive pump.
- His designs for canals and irrigation systems demonstrate knowledge of hydraulic power and its applications.
- He studied the flow of water through pipes and channels, analyzing resistance and velocity.
- Da Vinci’s work on the canals of Milan involved optimizing water flow for agricultural and civic purposes.
- His designs included systems for raising water to higher elevations using pumps and siphons.
- He investigated the use of water pressure for moving objects and powering machinery.
'
Mechanics
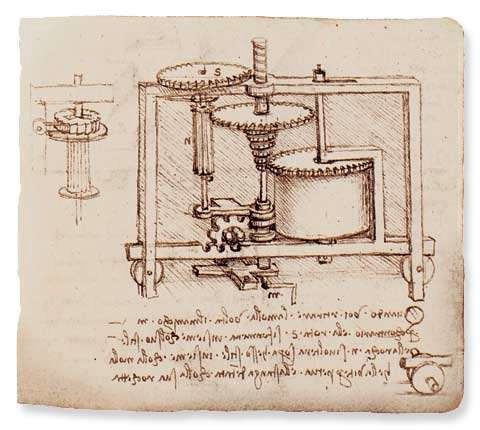
- Leonardo da Vinci was not only an artist, but also a talented inventor and scientist.
- He made significant contributions to the field of mechanics, including designing machines and studying the principles of movement.
- Da Vinci's detailed studies of anatomy and engineering helped him create innovative mechanical designs.
- One of his most famous drawings is the Vitruvian Man, which illustrates the ideal proportions of the human body.
- It is believed that Leonardo da Vinci's interest in mechanics and engineering played a major role in shaping his artistic works as well.
'
Goals and Aspirations
- Leonardo da Vinci was not only a painter, but also a sculptor, architect, inventor, and more.
- He had a curious mind and was always seeking to learn and understand the world around him.
- Da Vinci is known for his iconic paintings such as the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper.
- He kept detailed notebooks filled with sketches, scientific diagrams, and his observations on various topics.
- Da Vinci's interests ranged from anatomy and engineering to botany and geology.
'
Career Goals
- Da Vinci aimed to understand and depict the natural world with unparalleled accuracy, seeking to capture the essence of life and movement in his art and inventions.
- He was deeply interested in human anatomy, meticulously studying corpses to accurately represent the human form in his paintings and drawings.
- He sought to integrate art and science, believing that understanding the principles of mathematics, optics, and engineering were crucial to creating truly exceptional works of art.
- A significant goal was to develop new techniques in painting, particularly sfumato, to create realistic shading and a sense of depth.
- He aspired to create innovative machines and inventions based on his observations of nature and his understanding of mechanics, including flying machines, tanks, and automated devices.
- He envisioned himself as a universal man ("uomo universale"), possessing mastery over a wide range of disciplines, reflecting the Renaissance ideal.
- Da Vinci planned to publish a grand treatise on painting, outlining his theories and techniques, though this was never fully realized.
'
Innovation in Engineering
- Goals and Aspirations: Da Vinci possessed an insatiable curiosity and a relentless desire to understand the natural world and human anatomy. He sought to combine art and science, believing both were essential for a complete understanding of reality.
- Career Goals: His career goals centered around becoming a universal man – a polymath skilled in art, science, engineering, and anatomy. He aimed to achieve mastery in all these fields, driven by the belief that these disciplines were interconnected.
- Innovation in Engineering: Da Vinci's engineering innovations, though often unrealized during his lifetime, reflected a profound understanding of mechanics, hydraulics, and materials. He designed flying machines, tanks, submarines, and various automated devices.
- Emphasis on Observation and Experimentation: He heavily relied on meticulous observation and practical experimentation to develop his ideas, continuously pushing the boundaries of what was known at the time.
- Focus on Human Anatomy: A key aspect of his career goal was the extensive study of human anatomy, achieved through dissections, to improve his artistic skill and understand the mechanics of the body.
- Advanced Hydraulics: Da Vinci's designs incorporated complex hydraulic systems, reflecting deep knowledge of fluid dynamics and his inventive use of pumps and pipes.
'
Mastery of Art Techniques
- Leonardo da Vinci was a renowned Italian artist, known for his mastery of various art techniques such as painting, sculpting, and drawing.
- His famous works, such as the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper, showcase his exceptional skill and artistic vision.
- Da Vinci was a pioneer in techniques such as sfumato (blending colors seamlessly) and chiaroscuro (use of light and shadow to create depth).
- He was also a master of anatomical drawings, studying the human body in detail to accurately depict figures in his art.
- Da Vinci's notebooks, filled with drawings and notes on art techniques, offer valuable insights into his artistic process and experimentation.
'
Future Projects
- Title: Future Projects
- Current Path: Leonardo da Vinci\Goals and Aspirations\Future Projects
- Leonardo da Vinci was known for his diverse talents and interests, and he often had numerous projects in mind for the future.
- Some of his proposed future projects included architectural designs for cities, plans for flying machines, and ideas for innovative weaponry.
- Leonardo da Vinci's notebooks are filled with sketches and writings outlining his ambitious ideas for future projects.
- Although many of his future projects were never realized during his lifetime, his visionary concepts continue to inspire and fascinate people today.
'
Completion of Unfinished Works
- Leonardo da Vinci left many projects unfinished, including the famous painting "Adoration of the Magi."
- One of his most well-known unfinished works is "The Battle of Anghiari," a mural painting that was never completed due to various challenges.
- Da Vinci's fascination with the concept of flight led him to work on designs for flying machines which he never completed.
- Some art historians believe that da Vinci's habit of starting projects but not finishing them was due to his perfectionism and constant quest for knowledge.
'
Further Inventions and Discoveries
- Leonardo da Vinci is credited with inventing the concept of the parachute, designed to slow the descent of a falling person.
- He also conceptualized the idea of a self-propelled vehicle, similar to a modern-day car.
- Da Vinci created plans for a flying machine that closely resembled a modern-day helicopter.
- One of his notable inventions was the "robot knight," a mechanical device that could sit, stand, and move its head.
- Leonardo da Vinci's explorations and inventions laid the groundwork for many future discoveries in various fields.
'
Personal Goals
- Da Vinci’s primary goal was to achieve a comprehensive understanding of the natural world and human anatomy.
- He sought to master all arts and sciences, believing that the pursuit of knowledge in one field would enhance his understanding in others.
- A significant personal goal was to perfect his painting technique, striving for realism and capturing the essence of human emotion.
- He aimed to develop new and innovative inventions, including flying machines, armored vehicles, and diving apparatus.
- Da Vinci invested considerable time in studying the human body, driven by a desire to accurately depict it in his art and to understand its functions.
- He frequently documented his observations and sketches—a personal record of his continuous learning and experimentation.
- A goal was to elevate the status of art and science through integrated study.
'
Advancement of Scientific Knowledge
- Leonardo da Vinci is considered one of the greatest scholars of the Renaissance period.
- He made significant contributions to various scientific fields, including anatomy, engineering, and astronomy.
- Da Vinci's detailed anatomical drawings were used to further the understanding of the human body.
- His sketches of flying machines and war tools demonstrated his innovative approach to engineering and design.
- Da Vinci's notebooks contain a wealth of scientific observations and theories that were ahead of his time.
'
Exploration of Human Anatomy
- Leonardo da Vinci's exploration of human anatomy was revolutionary for its time, as he produced detailed and accurate anatomical drawings that were far ahead of his contemporaries.
- Da Vinci's studies included not only external anatomy but also internal organs and systems, such as the heart, brain, and reproductive organs.
- His anatomical drawings were not widely shared during his lifetime and remained largely unknown until centuries after his death.
- Da Vinci's work in human anatomy helped to advance the understanding of the human body and laid the foundation for future anatomical studies.
- His exploration of human anatomy also influenced his art, as he applied his knowledge of anatomy to create more realistic and accurate portrayals of the human form in his paintings and sculptures.
'
Health and Fitness
- Da Vinci was a meticulous observer of human anatomy, studying corpses to understand muscle structure and movement.
- He practiced gymnastics and fencing extensively, striving for physical prowess and understanding of human movement.
- Da Vinci employed rigorous training regimens, including running, swimming, and weightlifting exercises, to maintain physical fitness.
- His anatomical drawings were often based on dissections performed to improve training techniques.
- He documented his experiments with various physical exercises and their effects on the human body.
- Da Vinci's interest in proportion and balance influenced his designs for machines and structures, implicitly linked to the ideal human form and physical capability.
'
Physical Activity
- Leonardo da Vinci was known for his incredible athleticism and physical prowess.
- He was an avid runner and practiced long-distance running, often covering significant distances.
- He regularly swam, utilizing the water for both recreation and training.
- Da Vinci practiced gymnastics and acrobatic exercises, demonstrating impressive strength and agility.
- He incorporated physical training into his artistic endeavors, believing it contributed to his creativity and observational skills.
- Historical accounts suggest he undertook rigorous training regimens, including intense physical drills and exercises.
- His interest in anatomy fueled his physical training, as he studied the human body's movements and capabilities.
- He frequently engaged in activities like climbing and vaulting as part of his broader exploration of physical possibilities.
'
Fencing

- Leonardo da Vinci was known for his exceptional physical fitness for his time.
- He practiced fencing extensively, demonstrating remarkable skill and athleticism.
- He studied the mechanics of combat and human anatomy to improve his fencing technique.
- Da Vinci designed and built fencing equipment, including swords and protective gear.
- His fencing practice contributed to his understanding of movement, balance, and posture.
- He incorporated elements of martial arts and physical training into his overall fitness regime.
'
Horsemanship

- Leonardo da Vinci was incredibly athletic for his time, demonstrating a remarkable level of physical fitness.
- He practiced horsemanship extensively, studying anatomy of horses and perfecting riding techniques.
- Da Vinci engaged in rigorous physical activities as part of his training and observation of the natural world, including long distances riding.
- His physical activities were heavily influenced by his scientific investigations into human and animal movement.
- He consistently used physical exercise for health and well-being, demonstrating a proactive approach to fitness.
- Da Vinci's horsemanship was not merely a skill, but a deep study, involving detailed observations and practice of equestrian maneuvers.
'
Walking and Hiking
- Walking and hiking are great forms of exercise that can help improve cardiovascular fitness and muscle strength.
- Leonardo da Vinci was known to be a fan of walking and hiking, often using it as a way to explore nature and come up with new ideas.
- Walking and hiking are low-impact activities that can be enjoyed by people of all ages and fitness levels.
- Research has shown that walking and hiking in nature can help reduce stress and improve mental health.
- Walking is a fundamental human activity, and throughout history, humans have relied on walking as a primary mode of transportation.
'
Wellness Practices
- Leonardo da Vinci meticulously tracked his own physical condition throughout his life, documenting his weight, appetite, and health issues in a personal diary.
- He was known to practice daily exercise, including walking, running, and swimming.
- Da Vinci engaged in rigorous training for his military engineering projects, involving intense physical exertion and demanding physical capabilities.
- He paid close attention to diet, often consuming simple foods like bread, vegetables, and wine.
- He incorporated practices aimed at maintaining vitality, such as vigorous movement and attention to his physical state, prioritizing physical wellbeing.
- Da Vinci utilized techniques like massage and rest to promote recovery and alleviate physical strain.
- He valued the connection between mental and physical health, understanding the importance of balance.
- His meticulous record-keeping illustrates a proactive approach towards wellness and self-care.
'
Balanced Diet
- Leonardo da Vinci was known for his rigorous, almost obsessive, self-discipline regarding his health and fitness.
- He practiced daily walking and running, often covering considerable distances as part of his artistic and scientific investigations.
- Da Vinci meticulously tracked his food intake, documenting specific quantities and types of foods he consumed.
- He adhered to a largely vegetarian diet, minimizing meat consumption, likely due to health and philosophical reasons.
- His dietary staples included bread, fruits (apples, pears, grapes), vegetables (leeks, onions, asparagus), and cheese.
- He consumed a generous amount of water throughout the day to maintain hydration, vital for his extensive physical activity and artistic endeavors.
- Da Vinci observed and incorporated principles of balance into his lifestyle, seeking harmony between his physical, mental, and creative pursuits.
- His emphasis on consistent routines and mindful eating reflected a holistic approach to wellness.
- He valued rest and recovery, scheduling periods of inactivity to prevent exhaustion and maintain optimal health.
'
Mind-Body Connection
- Da Vinci meticulously tracked his own physical condition, detailing his weight, height, and overall health in journals.
- He practiced regular exercise, including walking, riding, and physical training, believing in the importance of a healthy body for a healthy mind.
- Da Vinci employed rigorous self-discipline in his training regimens, pushing himself to the limits of his physical strength and endurance.
- He utilized techniques resembling modern biofeedback, monitoring his body's responses to stress and adjusting his activities accordingly.
- Da Vinci valued restorative sleep and dedicated time to rest and relaxation, understanding the crucial role of recovery for optimal performance and mental clarity.
- He engaged in activities like meditation and contemplation, viewing them as vital for cultivating inner peace and strengthening the connection between his mind and body.
- Da Vinci's anatomical studies profoundly impacted his approach to wellness, recognizing the symbiotic relationship between the physical and mental aspects of human existence.
- He applied the principles of proportion and balance, both in art and in his personal life, reflecting a holistic understanding of the body's design.
- Da Vinci practiced dietary control, seeking to maintain a balanced and nutritious diet for optimal health and energy levels.
'
Personal Life
- Leonardo da Vinci was born on April 15, 1452, in Anchiano, near Vinci, Italy.
- His father, Piero da Vinci, was a notary and wealthy Florentine silk merchant.
- His mother, Caterina, was a peasant woman.
- He had five siblings: Giovanni, Antonio, Lucrezia, Girolamo, and Battista.
- He was largely educated by his father and a priest, Verrocchia.
- He apprenticed under Andrea del Verrocchio in Florence, learning painting, sculpture, and mechanics.
- He married Catterina Pergolesi in 1472.
- They had three children: Giovanni, Laura, and Sandro.
- His wife, Catterina, died in 1495.
- He had several known affairs, including with Lisa Gherardini (the model for the Mona Lisa) and a possible relationship with Isabella d'Este.
- He lived a somewhat reclusive life, spending much of his time in his studio and engaging in various projects.
'
Family
Here are some interesting facts about Leonardo da Vinci's family that you can include in your Sitemap:
- Leonardo da Vinci was the illegitimate son of a notary, Piero da Vinci, and a peasant woman named Caterina.
- He grew up in Vinci, a small town in Tuscany, Italy, with his father's family.
- Leonardo had 17 half-siblings from his father's numerous relationships, but he was the only child between his parents.
- He had a close relationship with his uncle, Francesco, who helped support his education and career as an artist.
- Leonardo da Vinci never married and had no children of his own.
'
Father: Ser Piero da Vinci
- Ser Piero da Vinci was an Italian notary, lawyer, and the father of the famous artist and inventor, Leonardo da Vinci.
- He lived in Vinci, a town in Tuscany, Italy, from which the surname "da Vinci" is derived.
- Ser Piero had a total of 17 children from various relationships, with Leonardo being the illegitimate son of Piero and a peasant woman named Caterina.
- Despite not having a close relationship with his son, Ser Piero financially supported Leonardo, ensuring he received a good education and opportunities to pursue his interests.
- Ser Piero da Vinci played a significant role in shaping Leonardo's early life, indirectly influencing the genius that he would become.
'
Mother: Caterina di Meo Lippi
- Caterina di Meo Lippi was the mother of the famous Italian polymath, Leonardo da Vinci.
- Little is known about Caterina di Meo Lippi, but it is believed that she was a peasant and worked as a local farmer.
- Leonardo da Vinci was closely attached to his mother and mentioned her in some of his journals and writings.
- Some researchers suggest that Leonardo's interest in nature and art was influenced by his mother who worked in the fields and countryside.
'
Siblings: 17 half-siblings
- Leonardo da Vinci had 17 half-siblings.
'
Hobbies and Interests
- Leonardo da Vinci had a wide range of hobbies and interests, including painting, sculpting, engineering, anatomy, and botany.
- He was particularly skilled at playing the lyre and also enjoyed singing.
- Da Vinci was an avid inventor, creating designs for flying machines, military weapons, and bridges.
- He had a fascination with nature and spent a great deal of time studying and sketching plants and animals.
- Da Vinci was known to be an excellent horseman and spent many hours riding and training horses.
'
Drawing

- Leonardo da Vinci was a master of the art of drawing, known for his precise and detailed sketches.
- He believed that drawing was the foundation of all forms of art and essential for understanding the world around us.
- Leonardo often used drawing as a way to study anatomy, nature, and engineering concepts
- His drawings are characterized by their use of light and shadow, creating a sense of depth and realism.
- Leonardo's drawings include sketches of inventions, botanical studies, and portraits.
'
Music

- Leonardo da Vinci was born on April 15, 1452, in Anchiano, near Vinci, Italy.
- He was illegitimate, the son of Ser Piero da Vinci, a notary, and Caterina, a peasant woman.
- He married Catterina Pergolesi in 1472.
- They had three children: Giovanni, Lucrezia, and Sandro.
- He was a skilled musician, playing the lira and possibly the viola.
- He composed musical pieces, including a "Madrigal".
- He studied music theory and practiced counterpoint.
- Leonardo's musical interests were intertwined with his scientific and artistic pursuits, possibly exploring the mathematical relationships within music.
'
Writing

- Leonardo da Vinci was an Italian Renaissance polymath, known for his expertise in various fields including painting, engineering, anatomy, and writing.
- His notebooks contain thousands of pages filled with sketches, scientific diagrams, and reflections on a wide range of subjects.
- Da Vinci was left-handed, and he often wrote his notes in mirror writing, a technique that made his writings difficult to decipher without a mirror.
- He had a fascination with flying machines and designed several prototypes for flying machines based on his observations of bird flight.
- Leonardo da Vinci's writing also included his thoughts on philosophy, music, and the nature of the universe, showcasing his diverse interests and intellectual curiosity.
'
Philosophy and Beliefs
- Leonardo da Vinci's philosophy emphasized the importance of direct experience and observation of the natural world.
- He believed in the concept of "Saper Vedere" which means "knowing how to see" and stressed the importance of using all the senses to truly understand the world.
- Da Vinci's beliefs often reflected his deep connection to nature and his fascination with the interconnectedness of all living things.
- His philosophical musings on subjects such as art, science, and nature continue to influence thinkers and creatives to this day.
'
Left-handedness
- Left-handedness is much less common than right-handedness, with only about 10% of the population being left-handed.
- Studies have shown that left-handed people may have a slight advantage in certain sports, such as tennis and baseball, due to the element of surprise against right-handed opponents.
- Although historically left-handedness was sometimes associated with negative connotations, it is now generally considered to be a normal variation in human handedness.
- Famous left-handed individuals include Leonardo da Vinci, Barack Obama, and Oprah Winfrey.
- Left-handed people are believed to be more creative and artistic, possibly due to the brain structure differences between left-handed and right-handed individuals.
'
Personal Journals and Writings
- Leonardo da Vinci kept numerous notebooks filled with his ideas, observations, and sketches.
- His journals also contained personal reflections, to-do lists, and even shopping lists.
- Da Vinci's journals were written in a unique mirror writing style, which was a way to protect his ideas from being easily understood by others.
- These writings offer valuable insights into his artistic process, scientific explorations, and philosophical musings.
- The notebooks cover a wide range of topics, including anatomy, botany, engineering, and even flying machines.
'
Vegetarianism
- Leonardo da Vinci was known to be a vegetarian for ethical reasons, believing that all living creatures should be treated with compassion and respect.
- His vegetarianism can be traced back to his childhood, where he would buy caged birds in order to set them free.
- Da Vinci's notebooks contain many writings on vegetarianism, advocating for the benefits of a plant-based diet both for the health of individuals and the planet.
- He often mentioned his love for animals and how he believed that humans should not harm or exploit them for their own purposes.
- This aspect of his philosophy is reflected in his artwork, where animals are often portrayed with tenderness and empathy.
'
Relationships
- Leonardo da Vinci was known to have had many close relationships with some of the most influential figures of his time, including benefactors, fellow artists, and scholars.
- One of Leonardo's most famous relationships was with Ludovico Sforza, the Duke of Milan, who commissioned him to create several works of art and engineering projects.
- Leonardo was also known to have had close relationships with other prominent artists such as Michelangelo and Raphael, with whom he shared ideas and collaborated on various projects.
- In addition to his professional relationships, Leonardo had several close friendships throughout his life, including his longtime companion and assistant, Francesco Melzi.
- Leonardo's relationships with his patrons and colleagues played a significant role in shaping his career and the influence of his work on future generations of artists.
'
Apprenticeship with Andrea del Verrocchio
- Andrea del Verrocchio was a renowned sculptor, painter, and teacher during the Italian Renaissance.
- Leonardo da Vinci, one of the most famous artists in history, was a prominent pupil of Verrocchio.
- During his apprenticeship with Verrocchio, Leonardo learned various artistic techniques and skills that would later influence his own works.
- Verrocchio's workshop was a hub of artistic innovation and creativity, where Leonardo collaborated with other talented artists.
- The apprenticeship with Andrea del Verrocchio was a crucial period in Leonardo da Vinci's artistic development and career.
'
Friendships with notable artists like Sandro Botticelli and Pietro Perugino
- Leonardo da Vinci formed a close friendship with the renowned Italian painter Sandro Botticelli, who was a major figure in the Florentine art scene during the Renaissance.
- Pietro Perugino, another notable artist, was also a friend of Leonardo da Vinci. Perugino was known for his contributions to the development of perspective in painting.
- These friendships with artists like Botticelli and Perugino likely had a significant influence on da Vinci's artistic style and approach to his own work.
'
Public Appearances
- Leonardo da Vinci was known for his diverse talents and was often invited to make public appearances at various events and gatherings.
- One of his most famous public appearances was when he showcased his flying machine designs to the public, demonstrating his innovative concepts and engineering skills.
- Leonardo's public appearances often drew large crowds who were fascinated by his artistic abilities, scientific knowledge, and inventive ideas.
- His public appearances not only showcased his talents but also helped him secure patrons and commissions for his work.
- Leonardo da Vinci's public appearances were a reflection of his status as a renowned artist, inventor, and thinker during the Renaissance period.
'
Exhibitions
- Exhibitions are a great way for artists to showcase their work to the public.
- Leonardo da Vinci's artworks have been featured in numerous exhibitions around the world.
- Public Appearances by artists like da Vinci can attract a large audience to exhibitions.
- Exhibitions often provide viewers with the opportunity to learn more about an artist's life and creative process.
- Attending exhibitions can inspire and enrich one's understanding of art and creativity.
'
Display of Artworks
- Display of Artworks is an essential part of the artistic process, allowing artists to showcase their creations to the public.
- Exhibitions provide a platform for artists like Leonardo da Vinci to share their work with a wider audience and receive feedback.
- Leonardo da Vinci's artworks have been displayed in various prestigious museums and galleries around the world.
- Public Appearances at art exhibitions can attract art enthusiasts, collectors, and critics, further enhancing the artist's reputation and recognition.
- The Display of Artworks allows viewers to appreciate the creativity, technique, and vision of the artist, offering a unique and enriching cultural experience.
'
Public Demonstrations of Inventions
- Public demonstrations of inventions by Leonardo da Vinci were a popular spectacle during the Renaissance period, showcasing his innovative ideas and designs.
- One of da Vinci's famous public demonstrations was the flying machine, which he designed based on his observations of bird flight.
- Da Vinci's public demonstrations often drew large crowds and fascinated onlookers with his visionary creations.
- These demonstrations not only entertained the public but also served as a way for da Vinci to showcase his talents and garner support from patrons.
- Many of da Vinci's inventions, demonstrated in public, laid the foundation for modern technologies and inspired future generations of inventors.
'
Interviews and Talks
- May 1, 1516: Leonardo da Vinci gave a lecture at the Château d'Amboise, France, to King Francis I and his court.
- 1517: He continued to give talks and lectures at the Château d'Amboise, engaging with European intellectuals.
- Several accounts describe da Vinci delivering on-the-spot demonstrations of his inventions and scientific theories during these public appearances.
- He often discussed his anatomical studies and engineering designs in detail during interviews.
- His presentations were known for their depth and intricacy, captivating his audience with demonstrations of his mechanical inventions.
'
Discussions on Art and Science
- Leonardo da Vinci was a Renaissance artist who was known for his expertise in both art and science.
- He was fascinated by the intersection of art and science, believing that the two disciplines were closely related and interconnected.
- Da Vinci's notebooks are filled with drawings and notes on topics such as anatomy, engineering, and physics, alongside his famous artworks like the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper.
- His studies of human anatomy greatly influenced his art, allowing him to create more realistic and detailed depictions of the human form.
- Da Vinci's understanding of mathematics and engineering also played a significant role in his artistic innovations, such as his use of perspective and light in his paintings.
'
Social Media
- Leonardo da Vinci did not use social media in the modern sense due to the invention of the internet and social media platforms.
- There are no documented records or evidence of da Vinci using platforms like Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, or any other contemporary social media sites.
- His communication primarily relied on letters, sketches, and direct observation of the world, methods predating digital social networking.
- While his anatomical drawings and scientific observations were widely disseminated through printed books and academies of the time, this differs significantly from the interactive nature of modern social media.
- His fame and influence were built upon his artistic and scientific achievements, not through online engagement.























